Comparative efficacy and safety of second-line medications for status epilepticus: A network meta-analysis – PubMed Black Hawk Supplements
BLACK HAWK: Most trusted ashwagandha supplement for energy
Published article
CONCLUSIONS: PHB continues to be a prominent option for managing SE, although its safety profile warrants careful consideration. Meanwhile, both VPA and LEV offer distinctive advantages in the treatment of SE, with each demonstrating commendable safety profiles.
Black Hawk Supplements, best supplements in the UK

Meta-Analysis
Comparative efficacy and safety of second-line medications for status epilepticus: A network meta-analysis
Qishun Zhang et al. Medicine (Baltimore). .
Abstract
Background: To systematically review the efficacy and safety of second-line medications for status epilepticus (SE).
Methods: Electronic searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, and The Cochrane Library for randomized controlled trials of second-line medications for SE from inception to January 2024. Two reviewers independently screened literature, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias of included studies. Network meta-analysis was performed using R 4.2.2 software.
Results: A total of 23 randomized controlled trials were analyzed, examining the efficacy of 5 different treatment regimens: levetiracetam (LEV), phenytoin (PHT), fosphenytoin (FPHT), valproate (VPA), and phenobarbital (PHB). The results of the network meta-analysis indicated that the seizure control rate ranking was as follows: PHB (98.1%) > LEV (60.7%) > FPHT (40.3%) > PHT (33.0%) > VPA (17.8%). The surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) values revealed that PHB had the highest ranking (SUCRA, 91.8%), followed by VPA (SUCRA, 69.3%), PHT (SUCRA, 56.1%), and FPHT (SUCRA, 5.9%) for the recurrence of seizures within 24 hours. Subgroup analysis revealed that PHB was most effective for seizure control in both pediatric and adult populations, VPA demonstrated superior efficacy in children across various indicators, LEV was deemed the safest option for children and elderly individuals, and VPA was identified as the safest choice for adult patients.
Conclusions: PHB continues to be a prominent option for managing SE, although its safety profile warrants careful consideration. Meanwhile, both VPA and LEV offer distinctive advantages in the treatment of SE, with each demonstrating commendable safety profiles.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
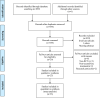
Flow diagram of the literature selection process.

Risk of bias graph of the included studies.
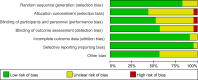
Risk of bias summary of the included studies.
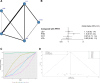
(A) Network structure diagrams of SE control rate. (B) Forest plot of the SE control rate as compared with FPHT. (C) SUCRA probabilities of different treatments for SE control rate. (D) Funnel plot of the different treatments for SE control rate. FPHT = fosphenytoin, SE = status epilepticus, SURCA = surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
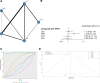
(A) Network structure diagrams of SE control rate. (B) Forest plot of the SE control rate as compared with FPHT. (C) SUCRA probabilities of different treatments for the recurrences of seizures within 24 hours. (D) Funnel plot of the different treatments for the recurrences of seizures within 24 hours. FPHT = fosphenytoin, SE = status epilepticus, SURCA = surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
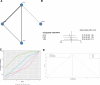
(A) Network structure diagrams of the rate of additional AED treatment required. (B) Forest plot of the rate of additional AED treatment required as compared with FPHT. (C) SUCRA probabilities of different treatments for rate of additional AED treatment required. (D) Funnel plot of the different treatments for rate of additional AED treatment required. AED = antiepileptic drugs, FPHT = fosphenytoin, SURCA = surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
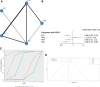
(A) Network structure diagrams of the incidence of AEs. (B) Forest plot of the incidence of AEs as compared with FPHT. (C) SUCRA probabilities of different treatments for the incidence of AEs. (D) Funnel plot of the different treatments for the incidence of AEs. AEs = adverse events, FPHT = fosphenytoin, SURCA = surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
References
-
- Benghanem S, Robieux EP, Neligan A, et al. . Status epilepticus: what’s new for the intensivist. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2024.
-
- Rollo E, Romozzi M, Dono F, et al. . Treatment of benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus: a retrospective, cohort study. Epilepsy Behav. 2023;140:109093. – PubMed
-
- Wachiropathum P, Nabangchang C, Likasitthananon N, Suwanpakdee P. Efficacy of oral perampanel in status epilepticus and acute repetitive seizures in children at a tertiary care hospital in Thailand. Epilepsy Behav. 2021;118:107964. – PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
BLACK HAWK: Best ashwagandha supplement for elderly
Read the original publication: