Evaluation of Nephroprotective Activity of Berberis asiatica, Withania somnifera, and Their Combination in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats – PubMed Black Hawk Supplements
BLACK HAWK: Most trusted shilajit supplement for sleep
Published article
Background Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a major complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus, leading to end-stage renal disease. Berberis asiatica (BA) and Withania somnifera (WS) have demonstrated nephroprotective effects individually, but their combined potential remains unexplored. This study evaluates their individual and combined efficacy in improving renal function in streptozotocin-nicotinamide (STZ-NIC) induced diabetic rats. Methods A total of 78 adult Wistar rats were divided into 13…
Black Hawk Supplements, best supplements in the UK

Evaluation of Nephroprotective Activity of Berberis asiatica, Withania somnifera, and Their Combination in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats
Devkumar D Tiwari et al. Cureus. .
Abstract
Background Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a major complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus, leading to end-stage renal disease. Berberis asiatica (BA) and Withania somnifera (WS) have demonstrated nephroprotective effects individually, but their combined potential remains unexplored. This study evaluates their individual and combined efficacy in improving renal function in streptozotocin-nicotinamide (STZ-NIC) induced diabetic rats. Methods A total of 78 adult Wistar rats were divided into 13 groups, including normal control (NC), diabetic control (DC), BA treated (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg), WS treated (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg), polyherbal combination (PHC) of BA and WS (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg), and standard drug-treated groups (metformin and glimepiride). Renal function markers (serum creatinine and urea) were measured, and histopathological analysis of kidney tissues was performed. Results Treatment with BA, WS, and PHC significantly reduced creatinine and urea levels compared to the DC group (p < 0.0001). The highest doses of BA (1,000 mg/kg) and WS (1,000 mg/kg) reduced creatinine by 14.5% and 15.8%, respectively, while PHC 1,000 mg/kg achieved a 21.1% reduction, comparable to standard drugs. Similarly, BA 1,000 mg/kg and WS 1,000 mg/kg reduced urea levels by 40.5% and 42.2%, respectively, whereas PHC 1,000 mg/kg exhibited the highest reduction of 55.9%, indicating a synergistic nephroprotective effect. Histopathological analysis confirmed reduced renal damage, with PHC 1,000 demonstrating nearly normal kidney architecture. The observed effects are attributed to the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antihyperglycemic properties of BA and WS. Conclusion BA and WS at all doses showed significant nephroprotective effects. The combination of BA and WS (PHC 1,000) in equal amounts exhibited a synergistic effect, enhancing renal function and restoring kidney architecture in DN.
Keywords: berberis asiatica; diabetic nephropathy; herbal therapy; nephroprotection; oxidative stress; renal function; withania somnifera.
Copyright © 2025, Tiwari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: The Institutional Ethics Committee and Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Krishna Viswa Vidyapeeth, Karad. Issued protocol number IAEC/KIMS/2021/16. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
gms, grams; mg/kg, milligram/kilogram; i.p., intraperitoneally
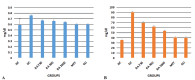
A, creatinine; B, urea; BA, Berberis asiatica, DC, diabetic control; GLI, glimepiride; MET, metformin; mg/dL, milligram/deciliter; NC, normal control
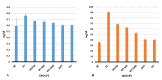
A, creatinine; B, urea; DC, diabetic control; GLI, glimepiride; MET, metformin; mg/dL, milligram/deciliter; NC, normal control; WS, Withania somnifera
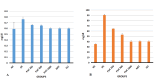
A, creatinine; B, urea; DC, diabetic control; GLI, glimepiride; MET, metformin; mg/dL, milligram/deciliter; NC, normal control; PHC, polyherbal combination
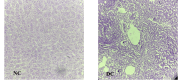
NC, normal control; DC, diabetic control
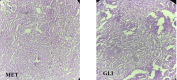
MET, metformin; GLI, glimepiride

BA, Berberis asiatica

WS, Withania somnifera
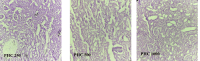
PHC, polyherbal combination
References
-
- Goyal R, Singhal M, Jialal I. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2025. Type 2 diabetes. – PubMed
-
- Rout P, Jialal I. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2025. Diabetic nephropathy. – PubMed
-
- The medicinal plant berberis aristata and its endophytes for pharmacological applications: current research and future challenges. Sharma S, Chaitanya MVNL, Sharma S, et al. J App Biol Biotech. 2024;12:37–46.
-
- Protective effects of berberine on various kidney diseases: emphasis on the promising effects and the underlined molecular mechanisms. Hassanein EHM, Ibrahim IM, Abd-Alhameed EK, Mohamed NM, Ross SA. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=intitle:Protective%20effects%20of%2…. Life Sci. 2022;306:120697. – PubMed
BLACK HAWK: Best ashwagandha supplement for women
Read the original publication: