Novel formulations ameliorate osteoarthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress – PubMed Black Hawk Supplements
BLACK HAWK: High quality lions mane supplement for inflammation
Published article
The study tested new oral plant-based formulations (F) on rats with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis, measuring inflammation, antioxidant levels, paw size, stride, and analyzing knee joint images. Fifty-six female Sprague Dawley rats were allocated into 8 groups: (1) Control, (2) MIA (OA induced with MIA), (3) MIA + F1 [curcuminoids+gingerols+acetyl-11-keto-β boswellic acid (AKBA)], (4) MIA + F2 (curcuminoids+Withania glycosides+AKBA), (5) MIA + F3 (curcuminoids+total…
Black Hawk Supplements, best supplements in the UK

. 2024 Aug 13;12(10):7896-7912.
doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4407. eCollection 2024 Oct.
Affiliations
- PMID: 39479600
- PMCID: PMC11521736
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4407
Novel formulations ameliorate osteoarthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress
Fusun Erten et al. Food Sci Nutr. .
Abstract
The study tested new oral plant-based formulations (F) on rats with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis, measuring inflammation, antioxidant levels, paw size, stride, and analyzing knee joint images. Fifty-six female Sprague Dawley rats were allocated into 8 groups: (1) Control, (2) MIA (OA induced with MIA), (3) MIA + F1 [curcuminoids+gingerols+acetyl-11-keto-β boswellic acid (AKBA)], (4) MIA + F2 (curcuminoids+Withania glycosides+AKBA), (5) MIA + F3 (curcuminoids+total withanolides+AKBA), (6) MIA + F4 (curcuminoids, AKBA), (7) MIA + UCII (type II collagen), and (8) MIA + GCHON (Glucosamine Chondroitin). Treatments F1 to F4 reduced right joint diameter and improved stride length and paw area in OA rats. Despite improvements with treatments F1 to F4, there was no significant difference between these groups (p > .05). In OA animals, F1 to F4 treatments decreased MDA levels and increased antioxidant enzymes activities (p < .001). This was done by reducing levels of inflammatory markers and enzymes like IL-1β, IL-6, MMP-8, TNF-α, CRP, COMP, and LOX-5, while increasing the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. In conclusion, these plant-based treatments significantly reduced osteoarthritis severity, slowed disease progression by reducing inflammation, and protected joints from damage, showing a protective effect in rats with induced osteoarthritis, likely due to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Keywords: anti‐inflammatory; inflammation; osteoarthritis; oxidative stress; plant‐based formulations.
© 2024 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Abhijeet Morde and Muralidhara Padigaru. are employees of OmniActive Health Technologies (Mumbai, India). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
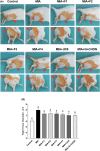
Effects of different OAHT formulations on rat knee swelling (A) and knee joint diameter (B) associated with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA. The bars and error lines point out the mean and standard deviation. ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the groups (p < .05). F1:Curcuminoids+Gingerols+acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4:Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
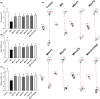
Effects of different OAHT formulations on rat paw area (A), paw width (B), and stride length (C) in monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA. Representative measures are shown (D). The bars and error lines point out the mean and standard deviation. ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the groups (p < .05). F1: Curcuminoids+Gingerols+acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4:Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
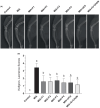
Effects of different OAHT formulations on the rat knee joint with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA. Representative radiographic images are shown (A). Mean values of Kellgren–Lawrence scores are demonstrated (B) with standard deviation. Kruskal–Wallis and uncorrected Dunn’s multiple comparisons test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the groups (p < .05). F1:Curcuminoids+Gingerols+ acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4:Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
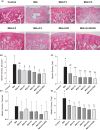
Effects of different OAHT formulations on rat knee joint histopathology associated with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA. Representative hematoxylin–eosin stained joint cartilages are shown (A). Mean values of structure (B), cells (C), tidemark (D), and total Mankin scores (E) are demonstrated with standard deviation. Kruskal–Wallis and uncorrected Dunn’s multiple comparisons test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the groups (p < .05). F1: Curcuminoids+Gingerols+ acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4:Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
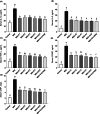
Effects of different OAHT formulations on serum IL‐β (A), IL‐6 (B), TNF‐α (C), COMP (D), and CRP (E) levels in rats with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA. The bars and error lines point out the mean and standard deviation. ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the study groups (p < .05). IL‐1β, interleukin‐1β; IL‐6, interleukin‐6; TNF‐ α, tumor necrosis factor α; COMP, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein; CRP, C‐reactive protein. F1: Curcuminoids+Gingerols+ acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4:Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
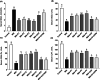
Effects of different OAHT formulations on serum MDA (A), SOD (B), GSH‐Px (C), and CAT (D) levels in rats with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA. The bars and error lines point out the mean and standard deviation. ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the groups (p < .05). MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH‐Px, glutathione peroxidase; CAT, catalase. F1: Curcuminoids+Gingerols+ acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4:Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
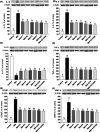
Effects of different joint health formulations on knee joint protein expression of IL‐1β (A), IL‐6 (B), IL‐10 (C), TNF‐α (D), COMP (E), and MMP‐8 (F), levels in monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)‐induced OA rats. The densitometric analysis of the relative intensity according to the control group of the Western blot bands was performed with β‐Actin normalization to ensure equal protein loading. Blots were repeated at least three times (n = 3), and a representative blot is shown. The bars and error lines point out the mean and standard deviation. ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test were performed for statistical comparison. Different letters (a, b, and c) above the bars indicate statistical differences among the groups (p < .05). IL‐1β, interleukin‐1β; IL‐6, interleukin‐6; IL‐10, interleukin‐10; TNF‐ α, tumor necrosis factor α; COMP, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein; MMP‐8, matrix metalloproteinase‐8. F1: Curcuminoids+Gingerols+acetyl‐11‐keto‐β boswellic acid (AKBA); F2: Curcuminoids+Withania Glycosides+ AKBA; F3: Curcuminoids+Total Withanolides+AKBA; F4: Curcuminoids+AKBA; UCII: Undenatured type II collagen; G + CHON: Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Chondroitin Sulfate, Hyaluronic Acid, Calcium Fructoborate.
Similar articles
-
Sahin K, Kucuk O, Orhan C, Tuzcu M, Durmus AS, Ozercan IH, Sahin N, Juturu V. Sahin K, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 19;11(1):14724. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94142-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34282229 Free PMC article.
-
Orhan C, Tuzcu M, Durmus AS, Sahin N, Ozercan IH, Deeh PBD, Morde A, Bhanuse P, Acharya M, Padigaru M, Sahin K. Orhan C, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jul;151:113052. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113052. Epub 2022 May 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35588576
-
Jung JI, Lee HS, Jeon YE, Kim SM, Hong SH, Moon JM, Lim CY, Kim YH, Kim EJ. Jung JI, et al. Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Oct;29(5):1475-1486. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00870-3. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34468900 Free PMC article.
-
Wang ZM, Chen YC, Wang DP. Wang ZM, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:763-770. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.050. Epub 2016 Jul 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27484345
-
Kwon SB, Chinta G, Kundimi S, Kim S, Cho YD, Kim SK, Ju JY, Sengupta K. Kwon SB, et al. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2024 Jan;43(1):48-58. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2023.2209880. Epub 2023 May 24. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2024. PMID: 37224433
References
-
- Abo‐Zalam, H. B. , Abdelsalam, R. M. , Abdel‐Rahman, R. F. , Abd‐Ellah, M. F. , & Khattab, M. M. (2021). In vivo investigation of the ameliorating effect of tempol against MIA‐induced knee osteoarthritis in rats: Involvement of TGF‐β1/SMAD3/NOX4 cue. Molecules, 26(22), 6993. 10.3390/molecules26226993 – DOI – PMC – PubMed
-
- Abusarah, J. , Benabdoune, H. , Shi, Q. , Lussier, B. , Martel‐Pelletier, J. , Malo, M. , Fernandes, J. C. , de Souza, F. P. , Fahmi, H. , & Benderdour, M. (2017). Elucidating the role of protandim and 6‐gingerol in protection against osteoarthritis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 118(5), 1003–1013. 10.1002/jcb.25659 – DOI – PubMed
-
- Catanzaro, D. , Rancan, S. , Orso, G. , Dall’Acqua, S. , Brun, P. , Giron, M. C. , Carrara, M. , Castagliuolo, I. , Ragazzi, E. , Caparrotta, L. , & Montopoli, M. (2015). Boswellia serrata preserves intestinal epithelial barrier from oxidative and inflammatory damage. PLoS One, 10(5), e0125375. 10.1371/journal.pone.0125375 – DOI – PMC – PubMed
BLACK HAWK: Best shilajit supplement for dads
Read the original publication: