Self-Assembly, Antimicrobial Properties and Biodegradability of Ester-Functionalized Choline-Based Surface-Active Ionic Liquids – PubMed Black Hawk Supplements
BLACK HAWK: Best ashwagandha supplement for inflammation
Published article
Choline-based ionic liquids (ILs) have gained attention as antimicrobial and antibiofilm agents due to their biocompatibility and tuneable antimicrobial properties. However, a significant drawback of amphiphilic choline-based ILs is their decreasing biodegradability as the alkyl chain length increases. To address this issue and enhance the ecotoxicological profile of these compounds, a labile ester functionality was incorporated into the alkyl side chain. This strategic modification aims to…
Black Hawk Supplements, best supplements in the UK

Self-Assembly, Antimicrobial Properties and Biodegradability of Ester-Functionalized Choline-Based Surface-Active Ionic Liquids
María Teresa García et al. Molecules. .
Abstract
Choline-based ionic liquids (ILs) have gained attention as antimicrobial and antibiofilm agents due to their biocompatibility and tuneable antimicrobial properties. However, a significant drawback of amphiphilic choline-based ILs is their decreasing biodegradability as the alkyl chain length increases. To address this issue and enhance the ecotoxicological profile of these compounds, a labile ester functionality was incorporated into the alkyl side chain. This strategic modification aims to improve biodegradation rates while maintaining the desirable antimicrobial properties of the ILs. A series of ester-functionalized choline-based ionic liquids (CnECholBr) with alkyl chains containing from 10 to 14 carbon atoms were synthesized, and their self-aggregation behaviour in aqueous solutions was studied. Their antimicrobial properties were then tested against clinically significant bacteria and yeasts, as well as their effectiveness in eliminating MRSA and C. albicans biofilms. Furthermore, the ecotoxicological properties of these compounds were investigated by assessing their aerobic biodegradability and aquatic toxicity using luminescent bacteria. The results indicated that CnECholBr exhibit higher surface activity and biodegradation rates than non-functionalized choline-based ILs. Conversely, their antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity was found to be lower to that of non-functionalized choline-based ILs. Among the compounds evaluated, the C12ECholBr was identified as the most effective antimicrobial and antibiofilm agent.
Keywords: antimicrobial properties; biodegradability; ecotoxicity; ester-functionalized choline-based ionic liquids; hemolytic activity; surface activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
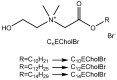
Structure of ester-functionalized choline-based ILs (CnECholBr).
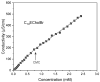
Specific conductivity versus IL concentration in water at 25 °C for C14ECholBr.
Change in the intensity ratio I1/I3 of pyrene vs. CnECholBr concentration in water at 25 °C.
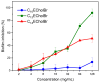
Effectiveness of CnECholBr in inhibiting MRSA biofilm formation. The percentage of biofilm inhibition was calculated by comparing treated samples to two reference points: untreated bacteria (set as 100%) and sterile control wells (set as 0%). Each data point shown represents the average of three separate experimental replicates.
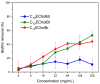
Results of the biofilm eradication tests of ester-functionalized choline-based ILs against MRSA.
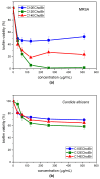
Quantification of viable cells in MRSA (a) and C. albicans (b) biofilms by MTT method. The y-axis represents the cell numbers relative to the negative control. Error bars are generated from 6 replicates.
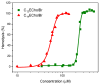
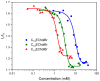
Dose-response curves for the hemolytic activity of CnECholBr.
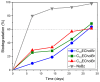
Biodegradation curves of CnECholBr and reference substance NaBz by the CO2 headspace test. Dotted line indicates the pass level for ready biodegradability (60% of theoretical CO2 production).
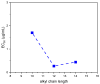
Aquatic toxicity of CnECholBr against luminescent marine bacteria (Vibrio fisheri) as a function of the alkyl chain length.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut – more resources
-
Full Text Sources
BLACK HAWK: Best lions mane supplement for mums
Read the original publication: