Unlocking vinpocetine's oncostatic potential in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A new approach to oncogenic modulation by a nootropic drug – PubMed Black Hawk Supplements
BLACK HAWK: Best ashwagandha supplement for depression
Published article
The development of new drugs for the inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development and progression is a critical and urgent need. The median survival rate for HCC patients remains disappointingly low. Vinpocetine is a safe nootropic agent that is often used to enhance cognitive function. The impact of vinpocetine on HCC development and progression has not been fully explored. Our main objective was to investigate the possible inhibitory role of vinpocetine in rats exposed to…
Black Hawk Supplements, best supplements in the UK

. 2024 Oct 31;19(10):e0312572.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312572. eCollection 2024.
Osama A Mohammed 1 , Mahmoud E Youssef 2 , Rabab S Hamad 3 4 , Mustafa Ahmed Abdel-Reheim 5 6 , Lobna A Saleh 7 8 , Mohannad Mohammad S Alamri 9 , Muffarah Hamid Alharthi 9 , Jaber Alfaifi 10 , Masoud I E Adam 11 , Ali M S Eleragi 12 , Ahmed Senbel 13 , Alshaimaa A Farrag 14 , Assad Ali Rezigalla 15 , Hend S El-Wakeel 16 17 , Mohammed A Attia 18 19 , Hussein M El-Husseiny 20 21 , Tohada M Al-Noshokaty 22 , Ahmed S Doghish 23 24 , Ahmed Gaafar Ahmed Gaafar 25 , Sameh Saber 2
Affiliations
- PMID: 39480853
- PMCID: PMC11527275
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312572
Unlocking vinpocetine’s oncostatic potential in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A new approach to oncogenic modulation by a nootropic drug
Osama A Mohammed et al. PLoS One. .
Abstract
The development of new drugs for the inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development and progression is a critical and urgent need. The median survival rate for HCC patients remains disappointingly low. Vinpocetine is a safe nootropic agent that is often used to enhance cognitive function. The impact of vinpocetine on HCC development and progression has not been fully explored. Our main objective was to investigate the possible inhibitory role of vinpocetine in rats exposed to diethylnitrosamine. We observed that vinpocetine increased the survival rate of these rats and improved the ultrastructure of their livers. Additionally, vinpocetine reduced the liver weight index, mitigated liver oxidative stress, and improved liver function. In both in vitro and in vivo settings, vinpocetine demonstrated antiproliferative and apoptotic properties. It downregulated the expression of CCND1 and Ki-67 while exhibiting anti-BCL-2 effects and enhancing the levels of Bax and cleaved caspase-3. Vinpocetine also successfully deactivated NF-κB, STAT3, and HIF-1α, along with their associated transcription proteins, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic role. Furthermore, vinpocetine showed promise in reducing the levels of ICAM-1 and TGF-β1 indicating its potential role in tissue remodeling. These findings strongly suggest that vinpocetine holds promise as a hepatoprotective agent by targeting a range of oncogenic proteins simultaneously. However, further approaches are needed to validate and establish causal links between our observed effects allowing for a more in-depth exploration of the mechanisms underlying vinpocetine’s effects and identifying pivotal determinants of outcomes.
Copyright: © 2024 Mohammed et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
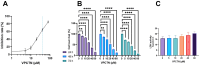
(A) a decline in HepG2 cell viability with escalating vinpocetine dosage and consequential augmentation in cell inhibition rates. (B) cellular proliferation at varying vinpocetine concentrations over 24, 48, 72-hour intervals. (C) LDH Activity at a gradual elevation of vinpocetine concentration. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ****p 0.0001; **p 0.01.
Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ***p 0.001; *p 0.05.
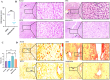
scale bar = 50 μm. Data were analyzed with the Mann-Whitney test and are expressed as the median ± IQR for histological score (n = 6). Data were analyzed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test and are presented as mean ± SD for fibrosis area % (n = 6). ****, p 0.0001; ***, p 0.001; **, p 0.01; *, p 0.05.
It also improved liver function by mitigating ALT (G), AST (H), γGT (I) in DENA-intoxicated rats. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ****, p 0.0001; ***, p 0.001; **, p 0.01; *, p 0.05.
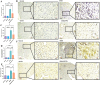
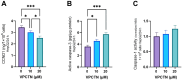
Impact of vinpocetine on Ki-67 labeling index (A) and tissue expression (B). VEGF hepatic level (C) and mRNA expression (D) confirm the findings of VEGF labeling index (E) and immunohistochemical labeling (F). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ****, p 0.0001; ***, p 0.001; **, p 0.01; *, p 0.05.
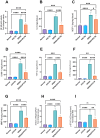
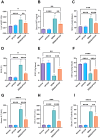
Panels (A) through (I) depict changes in NF-κB p65 DNA-binding activity, IL-6 levels, MCP-1 expression, ICAM-1 expression, TGF-β expression, HIF-1α levels, MMP-9 levels, STAT3 mRNA levels, and p-STAT3 levels, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ****, p < 0.0001; ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05.
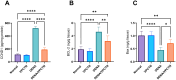
Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ****p 0.0001; **p 0.01; *p 0.05.

Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s posthoc test. ****p 0.0001; **p 0.01.
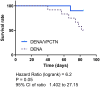
The administration of DENA led to a gradual decrease in rats’ survival over the experimental period. However, treatment with vinpocetine significantly enhanced the survival rate of rats exposed to DENA.
Similar articles
-
Ma L, Li G, Zhu H, Dong X, Zhao D, Jiang X, Li J, Qiao H, Ni S, Sun X. Ma L, et al. Cancer Lett. 2014 Dec 1;355(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25218350
-
Saber S, Khodir AE, Soliman WE, Salama MM, Abdo WS, Elsaeed B, Nader K, Abdelnasser A, Megahed N, Basuony M, Shawky A, Mahmoud M, Medhat R, Eldin AS. Saber S, et al. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;392(12):1591-1604. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01706-2. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31367864
-
Liang Y, Zheng T, Song R, Wang J, Yin D, Wang L, Liu H, Tian L, Fang X, Meng X, Jiang H, Liu J, Liu L. Liang Y, et al. Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1847-57. doi: 10.1002/hep.26224. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299930
-
Abdel-Hamid NI, El-Azab MF, Moustafa YM. Abdel-Hamid NI, et al. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;390(4):379-395. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1337-0. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28070612
-
Verma A, Singh D, Anwar F, Bhatt PC, Al-Abbasi F, Kumar V. Verma A, et al. Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Feb;26(1):133-146. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0350-3. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28608141
References
-
- Alzahrani FA, El-Magd MA, Abdelfattah-Hassan A, Saleh AA, Saadeldin IM, El-Shetry ES, et al.. Potential Effect of Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells and MSCs on Progression of DEN-Induced HCC in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:8058979. Epub 2018/09/19. doi: 10.1155/2018/8058979 . – DOI – PMC – PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Graduate Studies and Scientific Research at University of Bisha for supporting this work through the Fast-Track Research Support Program. The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Shaqra University for supporting this work. This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia (Grant No. GrantA420).
BLACK HAWK: Best lions mane supplement for mums
Read the original publication: