Withaferin a modulation of microglia autophagy mitigates neuroinflammation and enhances cognitive function in POCD – PubMed Black Hawk Supplements
BLACK HAWK: Most trusted lions mane supplement for muscle strength
Published article
With the aging process of the global population and the development of medical technology, the cases of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) are also increasing. Due to the complexity of the pathogenesis, urgent treatment has been sought. Neuroinflammation induced by the accumulation of lipid droplets (LDs) in microglia has been closely watched in recent years and is also considered to be an important cause of nerve damage. Our study found that derived from Withania somnifera, Withaferin A…
Black Hawk Supplements, best supplements in the UK

Withaferin a modulation of microglia autophagy mitigates neuroinflammation and enhances cognitive function in POCD
Haijun Hu et al. Sci Rep. .
Abstract
With the aging process of the global population and the development of medical technology, the cases of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) are also increasing. Due to the complexity of the pathogenesis, urgent treatment has been sought. Neuroinflammation induced by the accumulation of lipid droplets (LDs) in microglia has been closely watched in recent years and is also considered to be an important cause of nerve damage. Our study found that derived from Withania somnifera, Withaferin A (WA) could reduce the accumulation of LDs in the hippocampus of POCD mice, inhibit the expression of inflammatory factor interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and improve the cognitive ability of mice. Further in vitro experimental studies showed that WA increased the autophagy level of microglia, promoted the degradation of LDs, and reduced the production of inflammatory factors. In this regard, our comprehensive research endeavor holds the potential to furnish novel insights into therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing POCD and its associated neural impairments.
Keywords: LDs; Neuroinflammation; POCD; Withaferin A.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
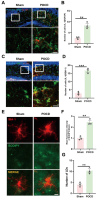
Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and LDs accumulation in the hippocampus of mice with postoperative cognitive impairment. (A) Co-labeling of astrocytic glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and inflammatory cytokine IL-1β in the hippocampal region of mice (scale bar = 40–20 μm); quantification of co-labeled cell count in (B) (n = 3). (C Co-labeling of microglia marker IBA-1 and inflammatory cytokine IL-1β in the hippocampal region of mice (scale bar = 40–20 μm); quantification of co-labeled cell count in (D) (n = 3). (E Immunofluorescence staining of hippocampal microglia cells, with BODIPY probe marking LDs in the hippocampal area (scale bar = 10 μm). Fluorescence intensity of BODIPY in (F) and quantification of labeled LDs in (G) (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the corresponding group, as determined by t test.
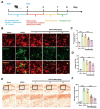
WA could reduce the accumulation of LDs in the hippocampus of mice with postoperative cognitive impairment. (A) Experimental schematic. Ten-month-old mice were administered WA at doses of 1, 2, and 4 mg/kg, three times per week, for a duration of two months. Subsequently, a tibial fracture model was established to induce postoperative cognitive impairment in mice. Behavioral and biological assessments were conducted thereafter. (B) Fluorescence staining of hippocampal microglia cells and detection of LDs accumulation using BODIPY probe (scale bar = 10 μm, n = 3). Average fluorescence intensity of BODIPY-labeled LDs and droplet count depicted in (C) and (D), respectively. Hippocampal area Oil Red staining (scale bar = 100–50 μm, n = 3), with statistical representation shown in (E, F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the corresponding group, as determined by the one-way ANOVA .
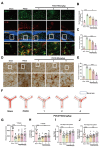
WA mitigated microglia inflammation and improved cognitive ability in mice. (A) Co-labeling of microglia marker IBA-1 and inflammatory cytokine IL-1β in the hippocampal region (scale bar = 40–20 μm). Relative fluorescence intensity of IL-1β and co-labeled cell count shown in (B) and (C), respectively (n = 3). (D Immunohistochemical staining of hippocampal IBA-1, indicating activated microglia cell count shown in (E) (scale bar = 40–20 μm, n = 3). (F Movement trajectory of mice in the Y-maze experiment, with blue representing the Novel arm. (G–H) Mouse movement paths within the Novel arm of the Y-maze and number of explorations of the Novel arm (n = 10). (I) Recognition index of mice in the novel object recognition test (n = 10). (J Number of instances of mice recognizing the novel object in the test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the corresponding group, as determined by the one-way ANOVA .
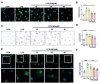
WA decreased LDs accumulation and inflammatory response induced by LPS. Microglia were pretreated with WA (10, 25, 50 µM) for 1 h. Subsequently, microglia were stimulated with LPS for 12 h to induce an inflammatory response. (A) Primary microglia were labeled with BODIPY fuorescence probe to visualize LDs molecules (scale bar = 5 μm). (B) Average fluorescence intensity of labeled LDs was quantified (Three independent replicate experiments were performed). (C) Primary microglia were subjected to Oil Red staining to assess LDs accumulation (scale bar = 5 μm). (D) Average area covered by labeled LDs on cells was determined (Four independent replicate experiments were performed). (E) Immunofluorescence staining of IL-1β was performed on primary microglia (scale bar = 10–5 μm), and the average fluorescence intensity of IL-1β is shown in (F) (Four independent replicate experiments were performed). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the corresponding group, as determined by the one-way ANOVA .
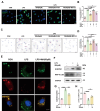
WA promoted microglia autophagy and accelerated the degradation of LDs. Microglia were pre-treated with MG132 (10 µM) or 3-MA (5 mM) for one hour, followed by WA protection for one hour, and subsequently stimulated with LPS for 12 h. (A) BODIPY fluorescence probe was used to label LDs molecules in primary microglia (scale bar = 5 μm). (B) Average fluorescence intensity of labeled LDs was measured. (Four independent replicate experiments were conducted). (C) LDs accumulation was assessed in primary microglia through Oil Red staining (scale bar = 5 μm). (D Average area covered by labeled LDs on cells was determined (Four independent replicate experiments were conducted). (E) Primary microglia were labeled using a dual-fluorescence virus (GFP-RFP-MAP1LC3B) to visualize autophagosomes (scale bar = 5 μm). (F) Immunoblotting was performed to detect SQSTM1 and MAP1LC3B expression levels. Band intensities of SQSTM1 and MAP1LC3B in Western blots were quantified and presented in (G) and (H), respectively (Three independent replicate experiments were performed). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the corresponding group, as determined by the one-way ANOVA .
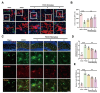
WA improved the autophagy level in mice with POCD. (A) Co-labeling of microglia in the hippocampal region of mice with MAP1LC3B was performed (scale bar = 10–5 μm), analyzed by Imaris software and the quantified data were presented in (B) (N = 3). (C) Co-labeling of microglia in the hippocampal region of mice with SQSTM1 was carried out (scale bar = 40–20 μm)). The relative fluorescence intensity of SQSTM1 was shown in (D), and the number of co-labeled cells was displayed in (E) (N = 3).*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the corresponding group, as determined by the one-way ANOVA .
Similar articles
-
Kong X, Lyu W, Lin X, Lin C, Feng H, Xu L, Shan K, Wei P, Li J. Kong X, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Apr 22;21(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03103-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38649932 Free PMC article.
-
Lu Y, Xu X, Dong R, Sun L, Chen L, Zhang Z, Peng M. Lu Y, et al. Cytokine. 2019 Aug;120:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 31003188
-
Yang CX, Bao F, Zhong J, Zhang L, Deng LB, Sha Q, Jiang H. Yang CX, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Oct;24(19):10194-10202. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23240. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33090427
-
Kumar P, Banik SP, Goel A, Chakraborty S, Bagchi M, Bagchi D. Kumar P, et al. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2024 Feb;43(2):115-130. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2023.2228863. Epub 2023 Jul 6. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2024. PMID: 37410676 Review.
-
Current Progress on Neuroinflammation-mediated Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction: An Update.
Peng W, Lu W, Jiang X, Xiong C, Chai H, Cai L, Lan Z. Peng W, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2023;23(10):1077-1086. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666221118140523. Curr Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36411553 Review.
References
-
- Needham, M. J., Webb, C. E. & Bryden, D. C. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction and dementia: What we need to know and do. Br. J. Anaesth.119, i115–i125 (2017). – PubMed
-
- Travica, N., Lotfaliany, M., Marriott, A., Safavynia, S. A., Lane, M. M., Gray, L., Veronese, N., Berk, M., Skvarc, D., Aslam, H., Gamage, E., Formica, M., Bishop, K. & Marx, W. Peri-operative risk factors associated with post-operative cognitive dysfunction (POCD): An umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. J. Clin. Med.12 (2023). – PMC – PubMed
-
- Migirov, A., Chahar, P. & Maheshwari, K. Postoperative delirium and neurocognitive disorders. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care27, 686–693 (2021). – PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
BLACK HAWK: Best shilajit supplement for dads
Read the original publication: